
Table of Content
Finance leaders do not have time to chase data across spreadsheets or fix manual errors that should not happen in the first place. RPA in finance helps by automating recurring work like reconciliations, automated financial reporting, and transaction monitoring. You gain more control without adding complexity.
According to Deloitte, finance teams still spend nearly 40% of their time on manual tasks that RPA can now fully automate. With the right finance automation tools, companies see 30 to 40% faster processing and a 90% drop in reporting errors. It becomes easier to manage compliance, speed up the audit process, and reduce risks.
This blog explains where intelligent automation in finance makes the biggest impact and how to put it to work inside your team.
RPA in finance uses software bots to carry out repetitive tasks that would otherwise need human input. This includes data entry, invoice processing, accounts reconciliation, and report generation. Instead of adding more staff to handle growing workloads, companies use RPA services to complete these steps faster, with fewer errors. The goal is not just speed, but consistency and control across every financial process.
| Manual Work | RPA |
|---|---|
| Accounts for 2%-5% of total errors per 100 tasks. | Finance Departments can save 25,000 Hours of Avoidable Work per year. |
| Contribute to $3.1 trillion in costs across U.S. businesses. | Equals a cost of $878,000 for an organization with 40 full-time accounting staff |
Traditional automation is built into the system. It works in the background using fixed logic but often needs IT to make changes or updates. That creates delays, especially when processes shift or exceptions occur.
RPA is more flexible. It runs on top of your existing tools, acting like a user clicking through screens, copying values, submitting entries. It connects easily with existing finance automation tools and helps streamline processes like automated financial reporting, audit process automation, and automation for accounts payable.
It also handles real-time tasks like automated transaction monitoring and supports financial data consolidation tools that pull from multiple sources. Most importantly, it works alongside compliance automation software to reduce risk without slowing teams down.
With AI software solutions and RPA in accounting, finance leaders gain consistency and visibility without restructuring core systems. That is the difference, traditional automation supports the system, while RPA supports the work.
| Aspect | Traditional Automation | RPA in Finance |
|---|---|---|
| System Integration | Requires integration into backend systems | Works on top of existing applications |
| Implementation Speed | Slower to deploy; needs coding and system changes | Quick to implement and scale with minimal disruption |
| Flexibility | Handles structured, rule-based inputs only | Adapts to variable inputs like PDFs, emails, and web forms |
| Development Effort | Needs developer resources and backend modifications | Uses low-code tools; mimics human actions without deep integration |
| Cross-System Operations | Limited to one system or API | Can operate across multiple systems and interfaces |
| Best Fit Use Cases | Static backend workflows | Repetitive, human-like front-office and finance tasks |
Finance teams are often expected to deliver speed, accuracy, and control at the same time. Manual workflows make that difficult. Errors in reporting, delays in reconciliation, or missed payment terms directly affect cash flow and credibility.
These are not just operational issues, they shape how leadership sees the numbers and how confident they are in the decisions that follow. Intelligent automation in finance addresses this by removing repetitive tasks from the equation. With the right finance automation tools, teams gain cleaner data, stronger oversight, and fewer surprises at month-end.
Most finance functions pull data from multiple platforms such as ERP, CRM, bank feeds, and procurement tools. When this happens manually, the risk of working with outdated or mismatched information increases. It slows down reporting and makes strategic planning unreliable.
RPA, combined with financial data consolidation tools, solves this by integrating sources and preparing a complete, real-time view of financial performance. Teams spend less time aligning spreadsheets and more time reviewing what matters.
Audit delays are usually caused by missing documentation or incomplete records. Teams spend days tracking approvals or justifying entries that should have been captured automatically. Audit process automation reduces this overhead by logging activities as they happen.
Combined with automated financial reporting, it ensures that every transaction, approval, and correction is tracked. This simplifies audit handovers and gives internal teams confidence in their controls.
When accounts payable runs on email trails and spreadsheets, the risk of duplicate payments or late fees increases. These problems affect vendor trust and working capital. RPA for accounts payable automates invoice matching, flags duplicates, and ensures approval steps are followed.
A digital workforce for finance handles entries, checks, and payment triggers so your team can manage exceptions, not transactions.
Delays in spotting unusual activity create both compliance and financial risk. Manual reviews cannot catch every issue in time. With automated transaction monitoring, bots review activity against business rules as it happens.
When used with compliance automation software, the system flags exceptions and routes them to reviewers without delay. This gives finance leaders live visibility into issues before they grow into problems.

Handling purchase orders manually is repetitive, exhausting, and prone to missteps. Especially in Fintech, where cash inflows and outflows are constant. Thus, creating, sending, and getting approval for purchase orders can become monotonous. However, with RPA implemented with AI, this process becomes a simple task. The bots cut the possibility of errors, capture data, and automate the approval process. It’s simple, effective, quick, and, best of all, cost-saving.
Invoice processing can feel like a never-ending chore. Especially when dealing with different formats and client-specific requirements. Financial organizations often need help to get invoices right the first time, leading to delays and rework.
RPA is an efficient way to pay bills. It ensures accuracy and speeds up approvals. Plus, when you integrate automated invoicing software with RPA, you can cut the maker-and-checker process. As the system matches invoices with relevant purchase orders seamlessly.
Accounts reconciliation is one of those tasks that can take hours and leave room for errors. It’s critical yet tedious, especially when dealing with many systems. It becomes more time-consuming when dealing with sub-companies with different accounting structures. RPA in Finance and Accounting can make this easier for you. RPA bots can log into various systems, audit, and reconcile data at every step with minimal human intervention. The bots ensure that everything is quick, consistent, and correct. It will only flag when something important needs your attention.
Managing accounts payable and receivable is like juggling—there are many moving parts, and if you drop one, the consequences can be severe. RPA bots can take over most of these tasks. This includes generating invoices, matching them to purchase orders, routing for approvals, and processing payments. Whether it’s outgoing documents or incoming ones, RPA handles it efficiently. Thus, reducing errors and speeding up the process.
Tax season doesn’t have to be stressful anymore. With RPA in Finance and Accounting, you can automate data collection for tax reporting, calculate tax liabilities, and even submit tax returns. This automation minimizes the risk of errors and ensures you meet all compliance requirements on time. RPA allows your finance team to focus on strategic tax planning rather than getting bogged down by repetitive, manual tasks.
Tracking and approving travel expenses can be a real headache. It can often delay reimbursements and cause frustration. However, with RPA in Finance and Accounting, creating and processing expense reports is straightforward and fast.
RPA compares given data against company policies. It informs your accounting team whether the expenses comply. This not only speeds up the reimbursement process but also ensures accuracy and adherence to company guidelines. The bots ensure all records follow company policies and even send automated alerts for discrepancies. This makes the entire travel and expense management process smoother, faster, and less prone to errors.
Payroll is one area where mistakes are not an option. Studies show that approximately 20% of payrolls have errors. Each of these payroll mistakes cost organizations $291 on average.
With RPA, you can avoid this. It can calculate wages, handle deductions, or ensure compliance with tax regulations. The result? Timely and correct payroll processing. This leads to happier employees and a smoother operation. RPA can manage these tedious tasks for hours on end without getting tired or making errors. Thus, making it an essential tool for any large financial institution.
Financial reporting involves gathering data from various sources, confirming it, and generating reports. When done manually, these tasks are time-consuming and prone to errors. RPA changes the game by automating this entire process, allowing for faster, more accurate report generation. This means your financial insights are more reliable. Thus, RPA enables better decision-making and strategic planning.
Accurate budget planning and forecasting are crucial for any business but need lots of data gathering and analysis. RPA can automate these tasks. It ensures you have detailed variance reports and accurate forecasts at your fingertips. RPA combines historical data with current information and allows for accurate comparisons and trend analysis. It enables better decision-making and improving your financial management processes.
The average financial firm spends $52 million per year on KYC compliance. For some banks, it can be up to $384 million on KYC compliance and Customer Due Diligence (CDD). That's huge. Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance is necessary but time-consuming. RPA can streamline KYC by automating the collection and verification of customer information. This not only reduces the time and resources needed but also minimizes costly errors. Faster KYC processes mean quicker customer onboarding and an improved experience.
When it comes to financial planning, you need accurate data and insightful analysis. RPA can gather, format, and add data from various systems. This allows for better forecasting and more informed decision-making. By automating these tasks, RPA ensures that your financial planning processes are faster and more reliable. Thus, with RPA, you get a clear view of your company’s financial health.
Additionally, Bancolombia developed a robo-advisor to guide Colombian investors in the stock market.
In finance, compliance and governance depend on consistent execution. Most failures come from missed steps, incomplete records, or unclear ownership. Manual processes cannot scale across fast-moving teams or multi-system workflows.
RPA solves this by enforcing rules, logging activity, and removing gaps that weaken oversight. It gives finance leaders control without creating more review layers or complexity.
Most finance professionals spend a large part of their day handling tasks that do not need judgment. Reviewing entries, chasing follow-ups, and updating trackers all drain time and focus. A digital workforce for finance can manage these tasks across systems, freeing up internal teams to review exceptions and focus on analysis. This improves overall output without increasing team size.
Delays in reconciliation, reporting, or approvals often come from manual handoffs. A task sits idle until someone remembers to act. RPA works with finance automation tools to keep these workflows moving without reminders. Bots complete steps instantly, validate data, and push tasks to the next stage. Teams finish work faster, and deadlines stop relying on overtime or catch-up rounds.
Strong governance depends on visibility. When approvals, exceptions, or escalations happen outside the system, there is no reliable audit trail. With compliance automation software, every action is logged in real time. Finance leaders can review what happened, when, and why without relying on memory or after-the-fact notes. This reduces internal review cycles and builds confidence in process controls.
Financial forecasting fails when inputs are incomplete or out of sync. Manual consolidation introduces timing gaps and version issues that weaken models. With automated financial reporting and intelligent automation in finance, data is updated consistently and delivered in the right format. That gives finance teams more accurate planning inputs and more time to respond when conditions shift.
Every finance leader knows where the team loses time. Rework, delayed approvals, manual reconciliations, and scattered data slow things down and put accuracy at risk. RPA changes that. It automates what does not need a person, so your team can focus on what does. This section walks through the outcomes finance teams see when they replace repetitive tasks with smart, rule-based automation. Let's now discuss benefits of employing RPA.
To begin your RPA journey, use these simple techniques:
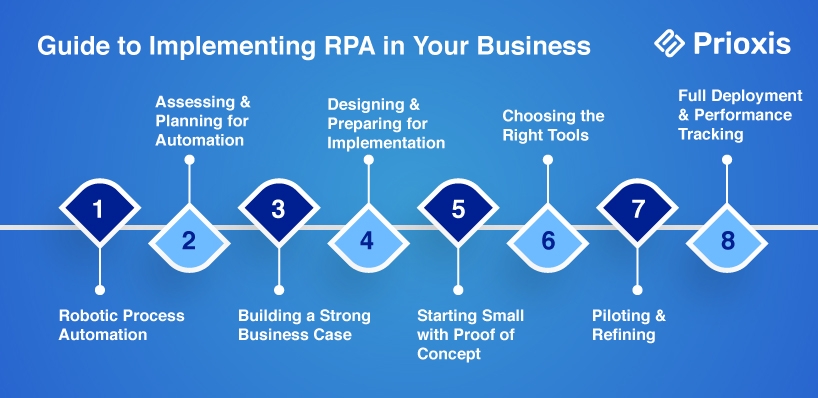
Begin by defining what you want to achieve with RPA. For instance, cutting costs, improving accuracy, or boosting efficiency.
Find the finance processes that will benefit most from automation. Make sure they align with your business goals.
Take a close look at your workflows to confirm that RPA can deliver real, measurable improvements.
Review your current processes to find routine, rule-based tasks that are good candidates for automation.
Consider each task's complexity, transaction volume, and impact.
Focus on tasks that offer the highest potential return on investment (ROI) to ensure you get the most out of your efforts.
Outline the benefits you expect from RPA. For instance, save money, increase productivity, and improve accuracy.
Prepare a detailed ROI analysis to show the financial value of the RPA project.
Find potential challenges and risks and plan how to manage them.
Create a clear implementation plan that includes timelines, resources, and risk management.
Design automation workflows that will integrate well with your existing systems.
Predict potential challenges in integrating RPA and plan how to address them.
Ensure your plan covers all aspects of deployment for a smooth rollout.
Begin with a small, practical application, like a basic bot, to test the feasibility of RPA within a few weeks.
This early project will give you hands-on experience and help you build excitement for the larger RPA program.
Select technologies that balance simplicity with effectiveness.
Start with a primary RPA platform. Then, complementary tools like process management or data recognition systems
Introduce more advanced tools as your program grows
Test the RPA system on a small scale to find and fix any issues.
Gather feedback from stakeholders and refine the processes.
Ensure the pilot is successful before rolling out RPA on a larger scale.
Roll out RPA across your finance department, ensuring smooth integration with existing systems.
Track the RPA system's performance and adjust it to keep it running efficiently.
When you choose an RPA tool for finance, it shouldn’t only be about automation, but also about finding the right system that understands how financial operations actually work. The wrong tool adds complexity. The right one helps you gain control, reduce errors, and scale without additional headcount. This section outlines the core features to expect and how top providers compare across real RPA use cases.
Not all RPA platforms are built for finance. Some offer broad capabilities but fall short when applied to reconciliation, compliance, or reporting cycles. A finance-focused tool should include:
More than features, the tool should support version control, access management, and built-in reporting dashboards so finance leaders can track process performance with minimal effort.
While most RPA tools claim to be finance-ready, a closer look often reveals major differences in use case maturity and support. Some are built for general process automation and require heavy configuration to suit finance needs. Others come with finance-specific modules ready to deploy.
Evaluation criteria include:
Leading providers tend to differentiate not on scale, but on how easily finance teams can use the platform without needing constant IT support. The best tool is the one that fits into your finance team’s workflow, not the other way around.
RPA needs to work with existing software. But many organizations struggle with compatibility issues because of different technologies and protocols.
Solution: Create a clear integration plan that outlines how RPA will connect with your existing systems. Find critical areas for integration. Test to ensure everything works together smoothly.
As businesses grow, RPA systems may need help to keep up with increased workloads, causing performance issues.
Solution: Plan for scalability right from the beginning. Use load balancing and track performance to tackle any bottlenecks before they affect operations.
Finding experienced RPA professionals can be difficult. This makes it hard to install and maintain the system.
Solution: Consider working with RPA service providers. They have an experienced team of RPA experts ensuring your project's success. Outsourcing RPA solutions to countries like India can also reduce costs.
RPA systems need regular maintenance, including updates and patches. Ignoring this can lead to errors and downtime.
Solution: Set up a maintenance schedule that includes regular updates and monitoring. RPA consulting can help keep your system running smoothly and securely.
Employees might resist adopting RPA. Because they fear for their job security or lack understanding of how the technology benefits them.
Solution: Communicate the benefits of RPA and involve employees in the process. Regular training sessions help ease concerns and build acceptance.
Not every process is suitable for automation, and picking the wrong ones can lead to project failure.
Solution: Analyze your processes to find the best candidates for automation. Focus on repetitive, high-volume tasks and avoid complex ones.
Organizations often need to pay more attention to the costs of implementing RPA. This can lead to budget issues and unmet return on investment (ROI) expectations.
Solution: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis before starting your RPA project. Consider both the first costs and long-term expenses like maintenance and operations.
A robust IT infrastructure is key to a successful RPA deployment, but outdated hardware or software can cause problems.
Solution: Review and upgrade your current infrastructure to ensure it can handle RPA workloads. Regular monitoring can help spot and fix issues before they become significant problems.
RPA systems can be vulnerable to cybersecurity threats if they’re not properly protected.
Solution: Install strong security measures, such as encryption and access controls.
Only 55% of organizations believe their automation efforts have been successful so far. Measuring the success of an RPA requires focusing on different metrics, depending on how mature the program is.
When starting with RPA, the focus should be on efficiency and productivity. Typical metrics include the number of automated tasks or bots deployed.
However, it’s also essential to consider the impact on employees. Such as how much time is saved on repetitive tasks and whether this has improved employee engagement.
As your RPA program grows, you’ll start to see improvements in compliance, such as fewer human errors and the creation of digital audit trails.
At this stage, you should track metrics that reflect these benefits. For example, compare the likelihood and cost of human errors before and after RPA implementation to see how much RPA has reduced errors.
When your RPA program is integrated and scalable across the organization, you’ll see extra benefits. For instance, reusable automation capabilities and cost savings.
Metrics at this stage should include
Implementing RPA is not just about deploying bots. It requires a clear strategy, ongoing oversight, and the right metrics to prove value at every stage.
Whether you are just getting started or expanding existing workflows, tracking the right indicators is essential to making automation work at scale.
At Prioxis, we bring over five years of experience in delivering successful RPA implementations across finance and operations. With a 99% success rate, we help teams move from planning to execution with confidence.
From early assessments to long-term optimization, our team can guide your RPA journey end to end. If you are looking for real results, we are ready to help you get there.
Get in touch