
Table of Content
To survive in the fast-moving logistics environment of today, shippers need to achieve total visibility and control over their supply chain networks to be efficient and more cost-effective at all times. This would be very hard to do without a single stream on which to run, thus enabling the identification of strong points, weak ones, and opportunities for improving transport operations.
A Transportation Management System (TMS) is the main tool that businesses use to streamline their logistics through shipments, tracking delivery, and optimizing routes. Initially, small businesses might get along on spreadsheets and manual procedures, but at some point, the expanded operation has to have a more sophisticated solution to handle those voluminous orders effectively.
In this guide, we will look at the basics of a Transport Management System, how a transport Management System works, what sets it apart from a WMS, its basic functions, and how to select the principal transportation & logistics software development company for your organization.
A transportation management system (TMS) is basically a software for businesses to plan, execute, and optimize the movement of commodities along the supply chain. The centralization of transportation information, automation of logistics processes, and enabling visibility of shipment have allowed businesses to drive efficiency while also reducing the transport management system cost.
TMS provides important transportation management functions such as routing, carrier selection, cargo tracking, freight bill auditing, and performance analysis. TMS guarantees that suppliers, carriers, and customers are all in sync since it seamlessly integrates with other supply chain solution software.
With the growing complexities in transportation and demand for quick deliveries, a TMS is needed by companies to optimize logistics operations, help in decision-making, and keep its market edge on the competition.
Transportation Management System (TMS) software is being used in many different kinds of businesses and organizations that need to plan, execute, and optimize the movement of goods that requires TMS users. TMS's main users are:
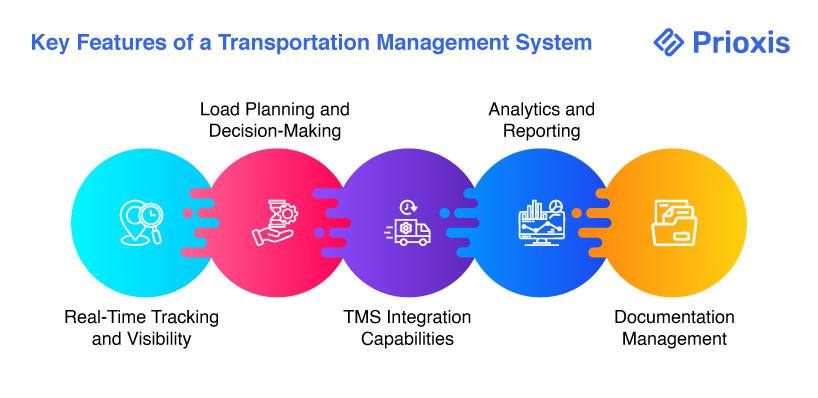
A transportation management system (TMS) refers to software that controls the transportation process in logistics, enhances visibility, and makes transportation operations more efficient. Some major functions of TMS and their contribution to supply chain efficiency are discussed below.
Thanks to TMS, businesses can track shipments in real time, giving them complete visibility in the supply chain. Using GPS tracking, automated notifications, and predictive analytics, companies might foresee delays, optimize delivery schedules, and enhance customer satisfaction. This feature is very much operationally transparent and helps with on-time deliveries.
To reduce transportation costs and improve efficiency, careful planning of the load is a must. The TMS automates the consolidation of shipments, selects carriers, and determines the best routes based on cost, distance, and delivery time. Hence, transport is an economical act engaging resources most efficiently while minimizing the empty miles.
A current TMS can be integrated with any of the other enterprise systems, such as the Warehouse Management System (WMS), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and eCommerce platforms themselves, enabling free-flowing data, greater coordination among departments, and proper handling of the supply chain. Connecting various operational tools creates streamlined workflows and coordination, thus improving overall efficiency.
Highly analytical and reporting-rich tools allow TMS to evaluate the essential performance indicators (KPIs), such as shipment times, freight costs, carrier performance, and fuel economy. Data insights help businesses identify areas for improvement, optimize their logistics strategies, and make data-driven decisions to increase transportation management efficiency.
The management of shipping documents, invoices, freight contracts, and compliance records is an integral part of logistics. A TMS simplifies this by generating documents automatically, digitizing records, and ensuring compliance with regulations. Thus, less paperwork, fewer mistakes, and improved operational viability will result.
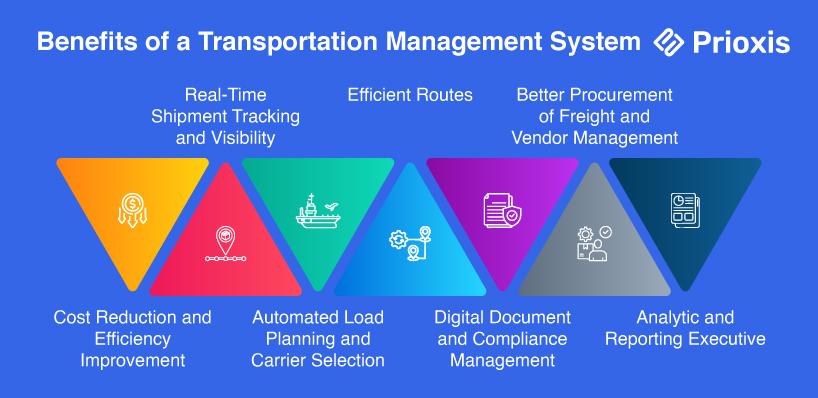
These are some of the major benefits of implementing a Transport Management System and its likelihood to revolutionize transportation and logistics management in shipping industries.
A TMS supports businesses by saving costs on freight transport through route optimization, cost-effective transportation carrier selection, and load planning automation. In AI-enabled dynamic routing, the algorithms consider fuel savings, emptied miles, and overall operational cost-saving techniques of the entire trip.
Built-in tracking features within TMS software can provide real-time shipment status updates to improve the accountability of the software. Businesses can track every point along the delivery process to guarantee a timely shipment and proactively mitigate a delay. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and a decline in shipment discrepancies.
Smart algorithms in TMS solutions enable automation load consolidation and carrier selection, resulting in reduced manual work and human error. The system assigns the shipment to the most appropriate carrier based on cost, delivery time, or shipment type and ensures a more efficient resource use.
With the input of AI-powered TMS Software, delivery points and all road conditions, as well as traffic patterns, are analyzed to define the best route possible. The system uses dynamic shifting to entrain real-time readjusting routes so that industries can avoid delays caused by congestion, bad weather, or road blockage.
Most often, paperwork can overburden the business performer in logistics. A TMS system would give them automated invoice generation, customs, and compliance paperwork with less room for manual error and faster processing time than before. All these have reduced the time of clearance and travel process time, and better compliance with regulations.
A TMS allows for comparing carrier rates, and there could be a better price negotiated with specific freight partners. Additionally, it would create a vendor management system through observing carrier performances to see if businesses are using the best service providers.
Data-driven insights let businesses track their key performance indicators like delivery time, carrier performance, and cost efficiency. This built-in analytics will help identify trends or inefficiencies so that organizations can make more intelligent and data-informed decisions, optimizing supply chain operations.
Progress has been made regarding transportation management systems (TMS). All the advances are possible because of changing technology. It includes smart routing, prediction analytics, and the automated decisions made by machine learning and AI. The Internet of Things integration will take real-time tracking to the next level and establish a blockchain as a part of the supply chain transaction for more transparency and security. TMS today will also be in the cloud, facilitating increased scalability and access to adjust to changing demands.
As logistics gets more complex, so does intelligence, necessitating intelligent TMSs in businesses that wish to continue succeeding. Investment in modern transportation management solutions ensures the optimization of operations, reduces costs, and enhances customer satisfaction: a hopeful portent for continued success in the logistics sector of the future.
Looking for a powerful, future-ready TMS? Prioxis delivers cutting-edge solutions tailored to your logistics needs. Experience seamless operations, cost savings, and enhanced efficiency with our innovative platform. Get in touch with our experts today and take your transportation management to the next level!
Get in touch